Understanding camera sensitivity is key for great photos. ISO is a basic concept in photography. It shows how well a camera picks up light. This lets photographers adjust their photos’ brightness.
Camera sensitivity is vital for photo quality. Knowing ISO helps photographers control light for their shots. It’s important for both new and experienced photographers to learn about ISO.
Learning about ISO is a big part of photography basics. It helps control the light in photos. With ISO knowledge, photographers can explore new creative ways to shoot.
Understanding ISO in Digital Photography
In digital photography, ISO is key to getting great photos. It shows how sensitive a camera’s sensor is to light. This is different from film photography, where ISO measured film sensitivity.
If you want to take nice images, you need to know about ISO. Light sensitivity, shutter speed, and ISO form the exposure triangle. Light is controlled by aperture and shutter speed, while the sensitivity to light is adjusted by ISO.
ISO’s role in digital photography has changed a lot. In film, ISO was fixed. But in digital, it can change with the light, making it more useful for photographers.
Definition of ISO in Photography
ISO measures how well a camera picks up light. In digital photography, it’s adjusted for the best image quality. This makes ISO a key part of the exposure triangle.
Historical Evolution from Film to Digital ISO
The shift from film to digital has changed ISO’s use. Now, digital cameras can adjust ISO for different lights. This lets photographers take great photos in many places.
The Role of ISO in Exposure Triangle
ISO is crucial in the exposure triangle for quality photos. By changing ISO, photographers can control image noise or grain. This is important for clear, high-quality digital photos.
How ISO Affects Image Quality
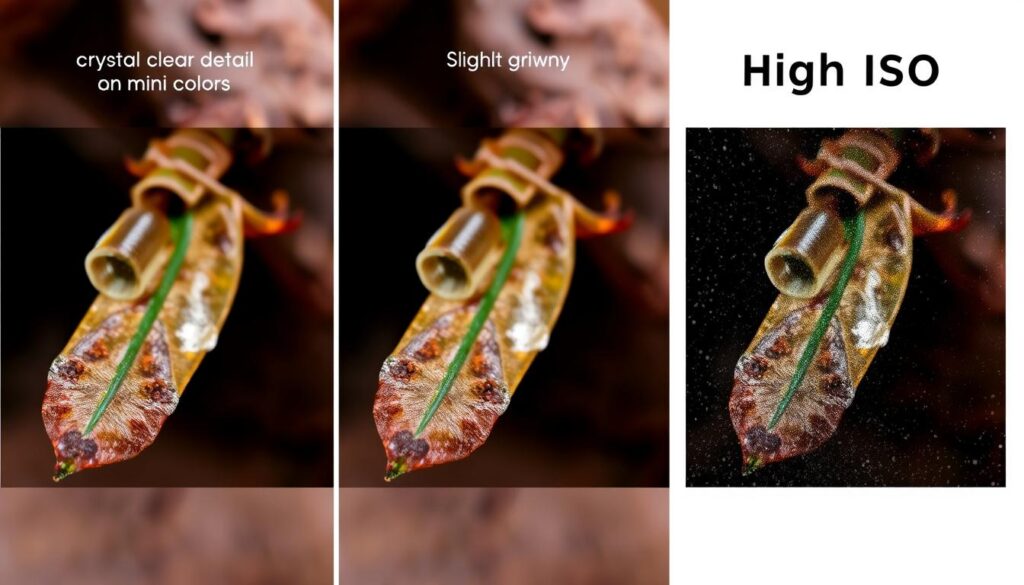
When it comes to photography, image quality is key. The ISO settings play a big role in this. ISO settings control how sensitive the camera is to light. Different ISOs can greatly change the image’s quality.
Low ISOs are best for bright light, giving you clear images with little digital noise. On the other hand, high ISOs are needed for dark places. But, they can add more digital noise, making the image less sharp.
Let’s look at some examples:
- ISO 100: Great for bright light, making images clear with little digital noise.
- ISO 6400: Good for dark places, but might add a lot of digital noise, hurting image quality.
Knowing how ISO settings affect image quality is crucial for photographers. It helps them choose the right ISO for the lighting. This way, they can reduce digital noise and get the best images for their work.

Science Behind ISO Sensitivity
Understanding how digital cameras handle ISO sensitivity is key for great photos. Digital sensors collect light and turn it into electrical signals. The camera’s native ISO shows how sensitive these sensors are, affecting the photo’s quality.
Signal amplification is also vital in ISO sensitivity. When ISO goes up, the camera can take photos in the dark. But, this can also add noise and lower image quality. To fix this, makers use special algorithms and better sensor designs.
Digital Sensors and Light Collection
Digital sensors have millions of photodiodes that turn light into electrical signals. The number and size of these photodiodes affect the camera’s ISO and photo quality. Some cameras have advanced tech like backside illumination to collect light better and reduce noise.
Signal Amplification Process
The signal amplification process boosts the electrical signals from the sensors. This lets the camera take photos in the dark. But, it also raises the chance of noise and image quality loss. To lessen this, makers use advanced signal processing and noise reduction.
Native vs Extended ISO
The native ISO of a camera is its sensitivity without amplification. Extended ISO uses amplification for higher sensitivities. While useful in some cases, extended ISO can add a lot of noise and lower image quality. Knowing the difference between native and extended ISO is crucial for better photos and less noise.
Common ISO Settings and Their Uses
Understanding ISO settings is key in photography. ISO settings control how sensitive the camera’s sensor is to light. Low ISOs are for bright light, while high ISOs are for dark light. The camera mode also affects the ISO setting.
Landscape photos need low ISOs for clear images with little noise. This is because landscapes are often well-lit.
ISO settings fall into three groups: low, medium, and high. Low ISOs (100-400) are best for bright scenes like landscapes and portraits. Medium ISOs (800-1600) work well for everyday shots like street and event photos. High ISOs (3200-6400) are for when it’s very dark, like indoor sports or concerts.
Here are some common ISO settings and their uses:
- ISO 100: Landscape, portrait, and studio photography
- ISO 400: Everyday photography, such as street and documentary photography
- ISO 1600: Low-light conditions, such as indoor events and nighttime photography
- ISO 6400: Extremely low-light conditions, such as astrophotography and nighttime sports photography
Knowing the different ISO settings helps photographers take better photos in all lighting. Whether using manual or automatic modes, the right ISO makes a big difference in photo quality.
Understanding ISO Noise and Grain
Photographers often face digital noise and grain when using high ISO settings. These can harm image quality. Digital noise is random pixel variations, while grain adds a film-like texture. Knowing how to reduce these is key.
Digital Noise Characteristics
Digital noise is more noticeable in low light. It looks like speckles or patterns. It comes from the camera’s sensor and amplification. To lessen it, photographers can adjust camera settings or use software.
Creative Uses of Grain
Grain can be good in black and white or portrait photos. It adds texture and depth. Some photographers aim for grain, while others avoid it.
Noise Reduction Techniques
To cut down digital noise, photographers have several methods:
- Adjusting camera settings, such as ISO and exposure compensation
- Using noise reduction software, like Adobe Lightroom or Nik Define
- Applying filters or plugins to reduce noise
Understanding digital noise and grain helps photographers choose the right ISO settings. This leads to better images with less noise.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Camera settings adjustment | Adjusting ISO, exposure compensation, and other camera settings to minimize digital noise |
| Noise reduction software | Using specialized software, such as Adobe Lightroom or Nik Define, to reduce digital noise |
| Filters or plugins | Applying filters or plugins to reduce digital noise and improve image quality |
Choosing the Right ISO for Different Scenarios
When picking an ISO, knowing the lighting and what you want to capture is key. Different photography scenarios need different camera settings for the best shots. For example, landscapes need a low ISO to show off the scenery. Portraits might use a higher ISO to freeze the moment.
For success in photography scenarios, making smart ISO selection choices is crucial. Here are some tips for different types of photography:
- Landscape photography: ISO 100-400
- Portrait photography: ISO 400-1600
- Sports photography: ISO 1600-6400
- Night photography: ISO 6400-12800
Adjusting your camera settings and ISO selection is vital. This way, photographers can take amazing pictures that reflect their vision.

Getting good at ISO selection takes time and effort. By trying out different camera settings and photography scenarios, photographers can find their style. They can then take pictures that tell a story.
| Photography Genre | Recommended ISO Range |
|---|---|
| Landscape | 100-400 |
| Portrait | 400-1600 |
| Sports | 1600-6400 |
| Night | 6400-12800 |
ISO Tips for Specific Photography Genres
Different photography genres need unique ISO settings. Knowing how to use ISO can greatly improve your photos. For landscape photography, a low ISO is best to keep scenes clear without noise. In contrast, sports photography and night photography often use higher ISOs to capture fast subjects and low-light scenes.
In portrait photography, the ISO depends on the lighting and the look you want. A lower ISO can make portraits look natural and flattering. A higher ISO can add drama and atmosphere. Here are some ISO tips for various photography genres:
- Landscape photography: Use a low ISO (100-400) to capture detailed images with minimal noise.
- Portrait photography: Use a medium ISO (400-800) to balance image quality and noise.
- Sports photography: Use a high ISO (1600-6400) to freeze fast-moving subjects and capture images in low-light conditions.
- Night photography: Use a high ISO (1600-6400) to capture images in low-light conditions, but be aware of the potential for noise and grain.
Understanding ISO for different genres can elevate your photography. You can create stunning images that show your creative vision.
| Genre | ISO Setting | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Landscape | 100-400 | Low ISO for detailed images with minimal noise |
| Portrait | 400-800 | Medium ISO for balanced image quality and noise |
| Sports | 1600-6400 | High ISO for freezing fast-moving subjects and low-light conditions |
| Night | 1600-6400 | High ISO for capturing images in low-light conditions |
Common ISO Mistakes to Avoid
Photography quality can suffer from ISO mistakes. One big error is using high ISOs in bright light, causing noise and grain. Always adjust your camera settings based on the light.
In order to avoid making mistakes, it is crucial to understand ISO. Avoid these pitfalls by keeping in mind these common mistakes:
- Using high ISOs in bright conditions
- Failing to adjust ISO when switching between indoor and outdoor shooting
- Not considering the impact of ISO on image noise and grain
By knowing these photography errors and adjusting your camera settings wisely, you can avoid ISO mistakes. Always think about the lighting and adjust your ISO to reduce noise and grain.
With practice, you’ll get better at setting your camera settings for top results. Don’t hesitate to try new things. By avoiding common ISO mistakes and mastering your camera settings, you’ll improve your photography skills.
Conclusion
Understanding ISO is key to taking amazing photos. It lets photographers explore new creative paths and make images that pop. We’ve seen how choosing the right ISO can change everything from exposure to artistic feel.
We’ve looked at ISO basics and how it fits into the exposure triangle. This knowledge helps you control your camera and reach your full potential. Whether it’s landscapes, portraits, or low-light shots, the right ISO can elevate your photos.
Learning to master ISO boosts your photography skills and gives you camera control. Knowing how ISO affects image quality and noise helps you tackle any shooting situation. You’ll be able to take photos that grab people’s attention.
FAQ
What is ISO in Photography?
ISO stands for International Organization for Standardization. It shows how sensitive your camera’s digital sensor is to light. It’s a key setting that affects how much light is needed for a good photo.
How Does ISO Affect Image Quality?
When you use a higher ISO, your camera’s sensor picks up more light. But, this can also make your photos noisier or grainier. It’s a balance between getting good photos in low light and keeping image quality high.
What Is the Difference Between Native and Extended ISO?
Native ISO is your camera’s base setting, offering the best image quality. Extended ISO is when you boost the sensitivity digitally. This can introduce more noise and reduce the photo’s dynamic range.
How Does ISO Interact with the Exposure Triangle?
Attributes of an exposure triangle include ISO, aperture, and shutter speed. Changing the ISO helps adjust to light changes. It’s about finding the right balance for quality, depth, and motion.
What Are Common ISO Settings and Their Uses?
ISO settings range from 100 to 12,800 or more, depending on your camera. Low ISOs (100-400) are for bright light and better image quality. High ISOs (800-12,800+) are for low light and fast subjects, focusing on getting enough exposure.
How Can I Reduce ISO Noise and Grain?
To lessen digital noise and grain, use lower ISOs, apply noise reduction in editing, and use camera features. Some photographers even like the look of grain and noise in their photos.
How Do I Choose the Right ISO for Different Photography Genres?
The best ISO varies by photography type. Landscape photographers use low ISOs for quality. Sports and wildlife photographers might use high ISOs for fast subjects in dim light. Knowing your genre’s needs helps choose the right ISO.
What Are Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using ISO?
Avoid using high ISOs in bright light, not adjusting ISO between indoors and outdoors, and ignoring ISO’s effect on quality. Being aware of these mistakes helps photographers make better choices and get better photos.





